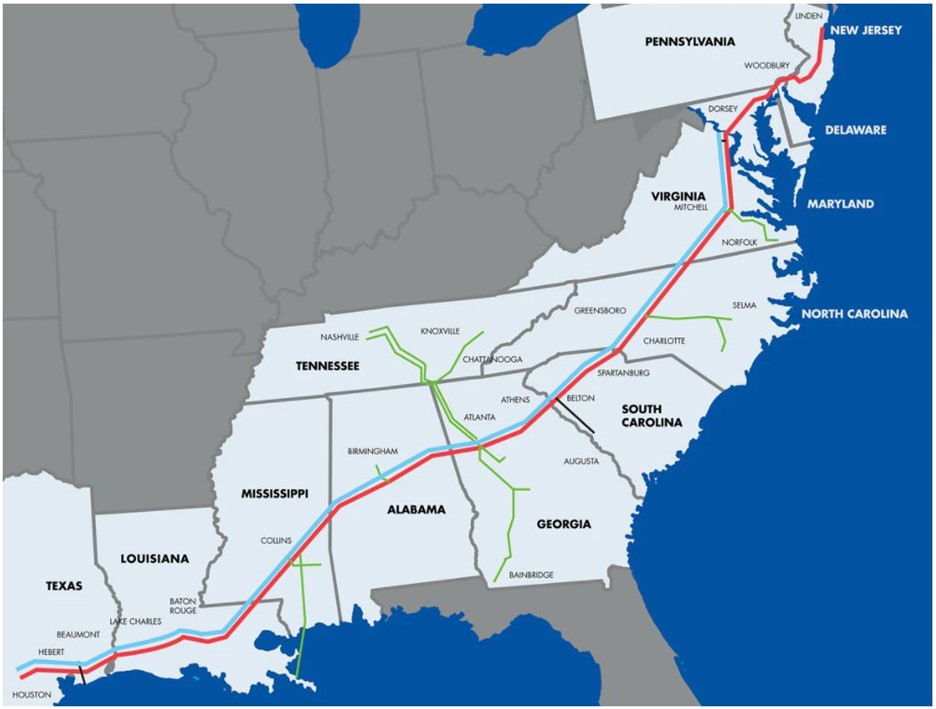
On May 7, the American company Colonial Pipeline stopped its work process due to a cyberattack initiated by ransomware. The cyberattack targeted the applications and systems responsible for controlling the procedure of pumping the oil derivatives through the pipelines that belong to the company, which are considered the longest pipelines in the United States, with a length of 8851 kilometers. The pipelines transport more than 378 million liters daily from Houston, Texas, to New York City’s port. Also, the company participates in 45% of the fuel spent on the East Coast of the United States.
The crisis included Alabama, Arkansas, the District of Columbia, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, New Jersey, New York, North and South Carolina, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Texas, and Virginia.
Cyberwarfare can be defined as actions by a country’s government to hack another country’s computers and private networks to cause damage or obstruction. Definitions may include non-state actors like terrorist groups, companies, political groups, extreme ideologists, criminal groups, and hacking activists.
The Effect of the Attack on Oil Prices
Jennifer Granholm, the spokeswoman for the US Department of Energy, said that she kept in contact with the CEO of Colonial Company to follow up on the progress that the company is making to neutralize the impact of the ransomware virus. She also mentioned:
“Even if the decision to reset the whole system were made, it would take many days to intensify the operation, even with the White House’s relaxing of the rules that are concerned with road transport that facilitate the flow of fuel to face the gas crisis in the East region”.
Even with the facilitations mentioned above, the restoration of the pipelines and their return to full service may take up to 14 days to transport the fuel stored in Houston until it reaches the filling stations. As for diesel and kerosene, ‘jet fuel’ will take up to 19 days since it is heavier and gets transported slower than the former.
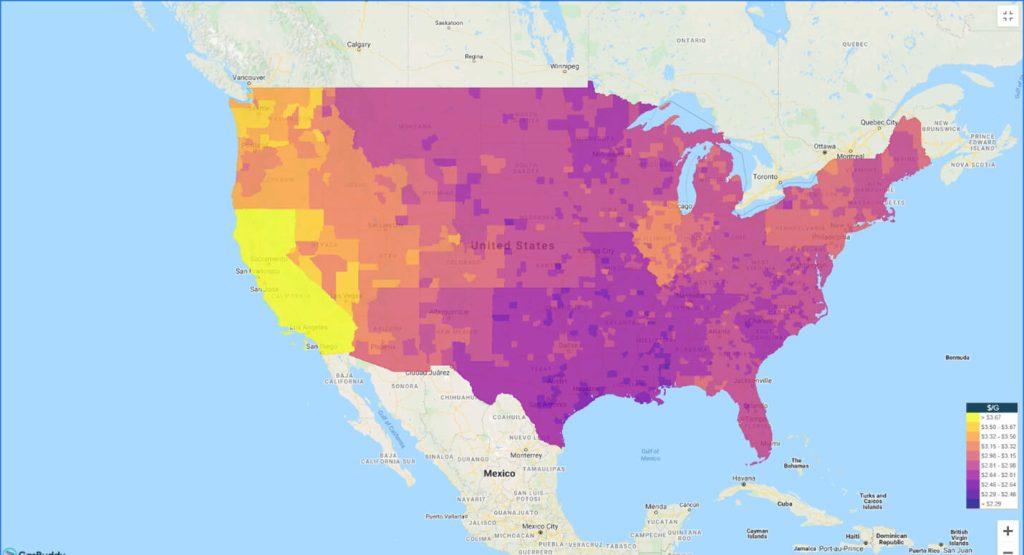
According to GasBuddy, a platform that keeps up with fuel prices, the rapid decrease in fuel in Atlanta was remarkable, for it had declined by 20% in filling stations.
The cyberattack has caused a rise in demand for gas in the affected states by between 20% and 40% and an increase of 11 cents daily in fuel prices in some regions. By the morning of the third day after the cyberattack, the gas had run out at 240 gas stations in Georgia, which equals almost 3.5%. In Virginia, the number was 7.5%, and in North Carolina, the state recorded a 5% rate of running out of fuel.
To sum up, and according to the heat map below, there is a fuel shortage in the affected states. It can be said that the cyberattack hit a sensitive location and caused a catastrophe in a short period of time. Here it can be visualized: what would happen if the cyberattack expanded and lasted for a more extended period?
What Had Happened?
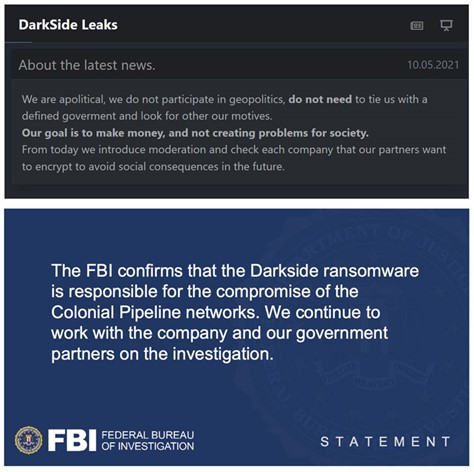
The company declared in a statement published on its online website that “on May 7, the company had been a victim to a cyberattack caused by ransomware, also known as a ransom virus,” that affected some information technology systems, which made it proactively shut down specific systems to contain the threat and temporarily stop all of the pipeline work that belongs to the company.
What should be touched upon here is that ransomware is considered malware that encrypts data files and attempts to take over files and applications using complex encrypted algorithms. As a result, the victim of this will not be able to reach, use, and edit these files, and the files cannot be decrypted unless a large amount of money is paid to the hacker; only then will the hacker decrypt the data files for the victim, who can once again access their data.
The Nature of the Attack and Who Stands Behind It?
The FBI has declared that the DarkSide criminal organization is responsible for the cyberattack. According to Mandiant, the Incident Response Section affiliated with the cybersecurity company FireEye contributed to the investigations.
As mentioned in the reports published by Bloomberg and The Wall Street Journal, the organization’s first criminal act was in August 2020; it targeted 91 locations. Notably, the DarkSide organization has revealed a code of conduct on the dark sites, conveying that they don’t target hospitals, schools, universities, elderly nursing homes, humanitarian organizations, or even governmental organizations.
Based on the FBI’s conclusions and the analysis of the previous cyberattacks initiated by DarkSide, it turned out that the organization is in association with Eastern European countries, for it was proven that it avoids targeting some countries depending on a tool that identifies the human language of the victim’s devices. It appeared to target English-speaking countries and avoid some parts of the former Soviet Union. This process is done based on the “white languages” list, meaning that the mother tongue and dialect are merged with other dialects and languages. This list is embedded in ransomware, including Russian, Ukrainian, Armenian, and Uzbekistanian, adding to them the Arabic language.
Additionally, it appeared that the DarkSide organization depends on encrypting the victim’s data by using specific algorithms that use aPLib to compress the configuration of the victim’s software. And a hybrid encryption system that uses RSA-1024 and Salsa20 to encrypt the data files and protect its keys asks for a ransom between 200 thousand dollars and 2 million dollars in exchange for decrypting the victim’s data.
On the other hand, some cybersecurity companies pointed the finger at Russia, even though the FBI declared that there is no clear evidence for these accusations. DarkSide has stated:
“We are not politicians, nor do we take part in geopolitics; also, we don’t need to be tied to a specific government, and we don’t seek other motivations,” adding: “Our goal is to gain money, not create troubles in society.”
Unrestrained Growth of Cyberattacks
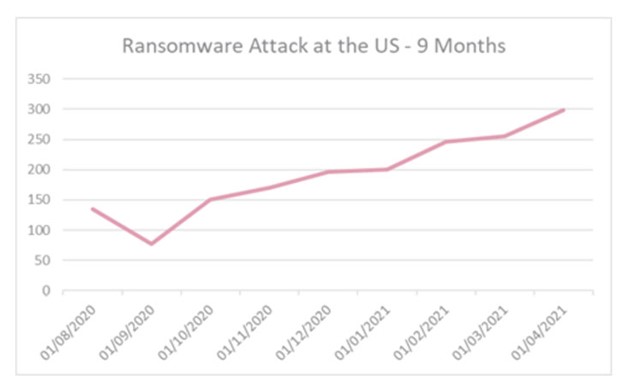
Based on a study conducted by Check Point and The Hacker News, there has been a notable rise in hacks of infrastructure and vital facilities. Also, the study revealed that cyberattacks have increased by up to 50% as an average of weekly attacks. Furthermore, the number of cyberattacks in which the ransomware virus is used has tripled during the last nine months.
A report by Cybersecurity Ventures in 2017 predicted that ransomware would cause a loss of 5 billion dollars annually, especially with its continual increase.
Expectations have indicated that losses may reach twice their number, reaching about 20 billion dollars during 2021; hence, recording an increase of losses 57 times what it had recorded in 2015. Cyberattacks using ransomware are anticipated to reach one attack every 11 seconds by the end of 2021.
The problem is that these cyberattacks are not limited only to financial losses but also include the cost of leaking or losing data, the time lost because of work stoppages, loss in productivity, obstruction of the typical workflow, restoration of lost data, and stolen systems, the time period needed for recovery and getting back to the same productivity level before the cyberattack, and further, the damages that will affect the reputation and the training of workers in the process of direct response to these attacks.
The United States is Not Safe!
The previously mentioned cyberattacks on the infrastructure are not incidents that only happened once. For instance, last February, a water treatment station faced a cyberattack by taking control of the water treatment system and increasing the level of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) from 100 parts per million, which is the amount used for water sterilization, to 11100 ppm. This change can cause severe poisoning cases and skin and eye irritations.
The Cyber Defense
In the past three years, the government of the United States has signed defense contracts with the most significant cybersecurity companies to protect government institutions and infrastructure. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has published several regulations and guidelines to minimize the danger of cyberattacks against power stations, oil refineries, and sensitive locations that could affect the public security of the United States.
In addition to the above, it is considered important to continue to digitalize data, i.e., transform it and use it digitally in all aspects of life. However, digitalizing the data resulted in the databases of the United States becoming targets of cyberattacks and cyberwarfare.
For years, the United States has seen these cyberattacks as a significant concern. Not only did this increase the frequency of data hacking, but it also increased its complexity and economic impact. Also, based on the Global Cybersecurity Index for 2019, the United States is considered one of the countries that give cybersecurity great attention. The government has spent 88 billion dollars on information technology, which is anticipated to reach 92 billion dollars by 2021.
As for allocating the budget, the role of the Department of Defense comes into play, for this department is the primary recipient of federal spending on cybersecurity, and it’s the agency’s responsibility to protect the United States from cyberattacks on the internet.


Federal agencies reported 13,107 cybersecurity events in 2018, and in the following year, the States accounted for 5.6% of the hacked data globally and 2.1% of all violations of the exposed records.
The hacking of the American voter database in December 2015 is considered one of the biggest data violations on the internet all over the globe. This incident received great attention because the connection between cybercrime and the American election process gained international attention during the 2016 presidential elections. This incident was the gateway for cyberattacks to set foot in the world of politics.
Resources and References
Ransomware Cyber Attack Forced the Largest U.S. Fuel Pipeline to Shut Down
Alert (AA20-049A) Ransomware Impacting Pipeline Operations
https://us-cert.cisa.gov/ncas/alerts/aa20-049a
Pipeline Cybersecurity Resources Library
https://www.cisa.gov/pipeline-cybersecurity-library
21-015 Detectives Investigate Computer Software Intrusion at Oldsmar’s Water Treatment Plant
Hacker Tried Poisoning Water Supply After Breaking Into Florida’s Treatment System
https://thehackernews.com/2021/02/hacker-tried-poisoning-water-supply.html
Recommendations Following the Oldsmar Water Treatment Facility Cyber Attack
https://www.acronis.com/en-us/articles/darkside-ransomware
Florida Water Treatment Plant Hit With Cyber Attack
https://www.industrialdefender.com/florida-water-treatment-plant-cyber-attack
How a Security by Design Approach Might Have Stopped the Florida Water Facility HMI Attack
U.S. Declares Emergency in 17 States Over Fuel Pipeline Cyber Attack
https://thehackernews.com/2021/05/us-declares-emergency-in-17-states-over.html
U.S. government and cyber crime – Statistics & Facts
https://www.statista.com/topics/3387/us-government-and-cyber-crime/#dossierSummary
Cyber security spending of the U.S. government on CFO Act and non-CFO Act agencies from FY 2018 to FY 2021
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1003402/us-cyber-security-spending-cfo-act-agencies
Global Ransomware Damage Costs Predicted To Reach $20 Billion (USD) By 2021
DarkSide Ransomware Does Not Attack Hospitals, Schools and Governments

